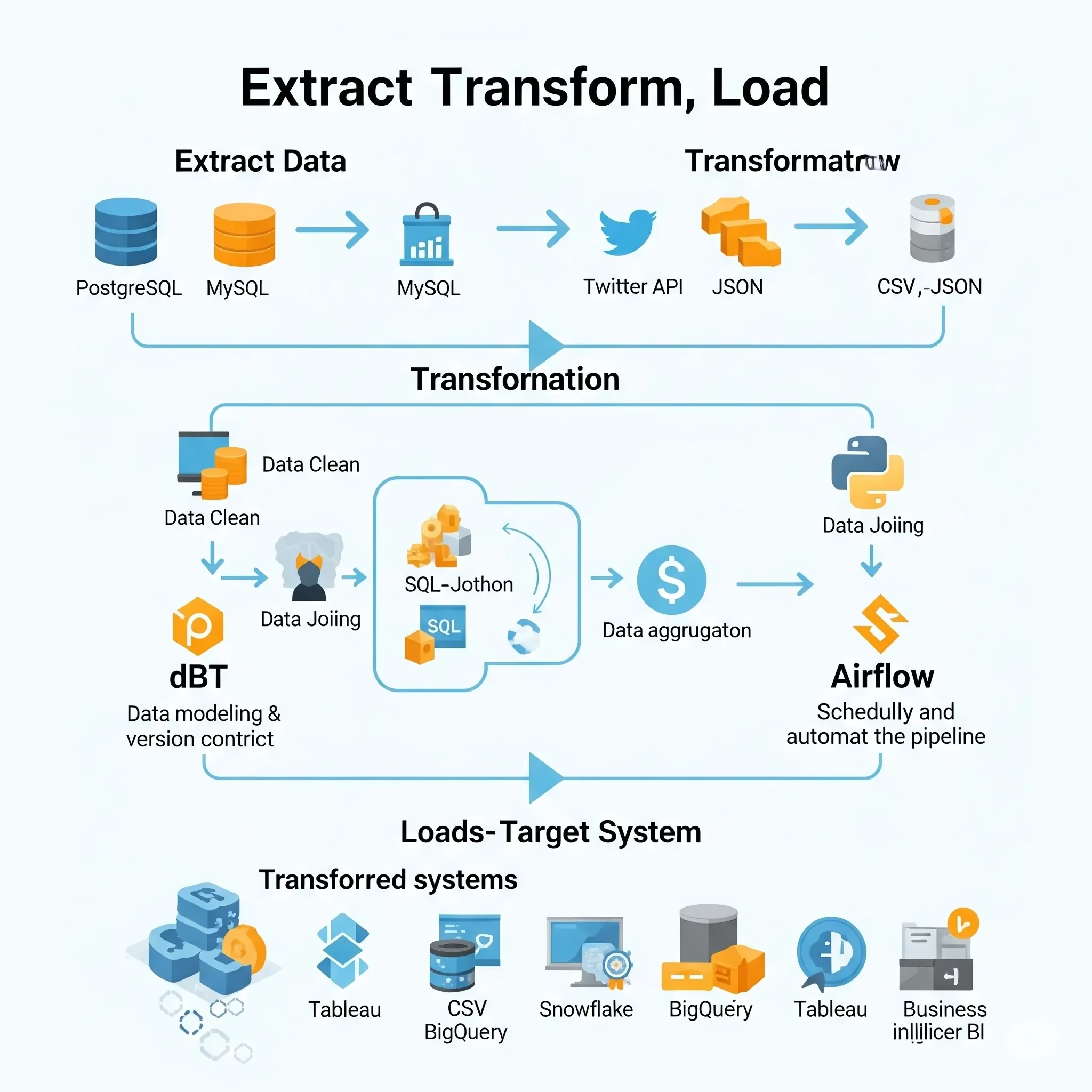
ETL for Data Analysts: What is the Pipeline?
In a data-oriented world, knowing how data flows is crucial; more for data analysts whose sole work is based on clean, well structured datasets. One of the most basic things that happen in the analytics stack is ETL; Extract, Transform, Load. Whether you’re examining customer behavior, predicting sales, or creating dashboards, you’re probably using data that has gone through an ETL pipeline.
In this post, we’ll be breaking down what makes the ETL process so mysterious and how it fits into a data analyst’s toolbox.
What is ETL?
ETL is a three part process used to move raw data into a form suitable for analysis and reporting:
Extract: Retrieve data from input systems.
Transform: Clean, enhance, and structure the data.
Load: Place the transformed data into a targeted operating system such as a data warehouse or an analytical data store.
This is to maintain the consistency, quality and useability of the data between the systems.
Step 1: Extract – Collecting Raw Data
The first step is data extraction from one or various sources. These could be:
By design, extraction is intended to have minimal impact on source systems; therefore, one must consider source data system implications and constraints. To analysts, knowing where the data comes from is important for context and for trusting their analysis.
Step 2: Transform – Cleaning and Shaping Data
This is where raw data becomes information ready for analysis. Transformation includes:
This is often the most tactile part, for analysts. Versioned and documented transformation Whatever the tool be it SQL, Python or BI tool, transformation transforms your dataset into the usable format.
Step 3: Load – Get data to a destination
The last step is to load the transformed data into a target system (which can be)decryptor or target system may be set of some applications etc.
The manner in which to load depends on the use case – some organisations require real-time ingest, others are happy with batch loads once per night.
ETL for Data Analysts It's worth starting by considering the world of Data Analysts.
Even if you never create another ETL pipeline, knowing how to means that you can:
A solid understanding of ETL means that you’re not just consuming data, but rather you’re a data partner inside of your organization.
ETL vs ELT: A Modern Twist
With new-age cloud infrastructure, there’s a shift from ETL to ELT, which stands for Extract, Load and then Transform. In ELT, data is first brought into an intermediary and then transformations are done via powerful computation engines.
The popularity of tools like dbt (data build tool) around this paradigm indicates a growing community of analysts who can be directly involved with transformation logic via versioned SQL.
Popular ETL Tools
Some ETL tools you might come across:
Knowing where these tools fit into your data stack allows you to trace data lineage and work more collaboratively across the organization.
Final Thoughts
ETL is the quiet savior of data. Data analysts need to know (and not just be “encouraged” to learn) the ETL pipeline. And it fills the rift between data and meaning – enabling you provide reports and dashboards with confidence.
Therefore, when you make time to understand how ETL works, you have officially upgraded yourself from number pusher to data strategist.
If you’re looking to acquire these skills hands-on, especially working with real-world data and tools such as SQL, dbt, and Airflow, check out a Data Analyst Training in Hyderabad. An organized curriculum can help accelerate your learning and get you ready for work in the world’s best data-driven companies.