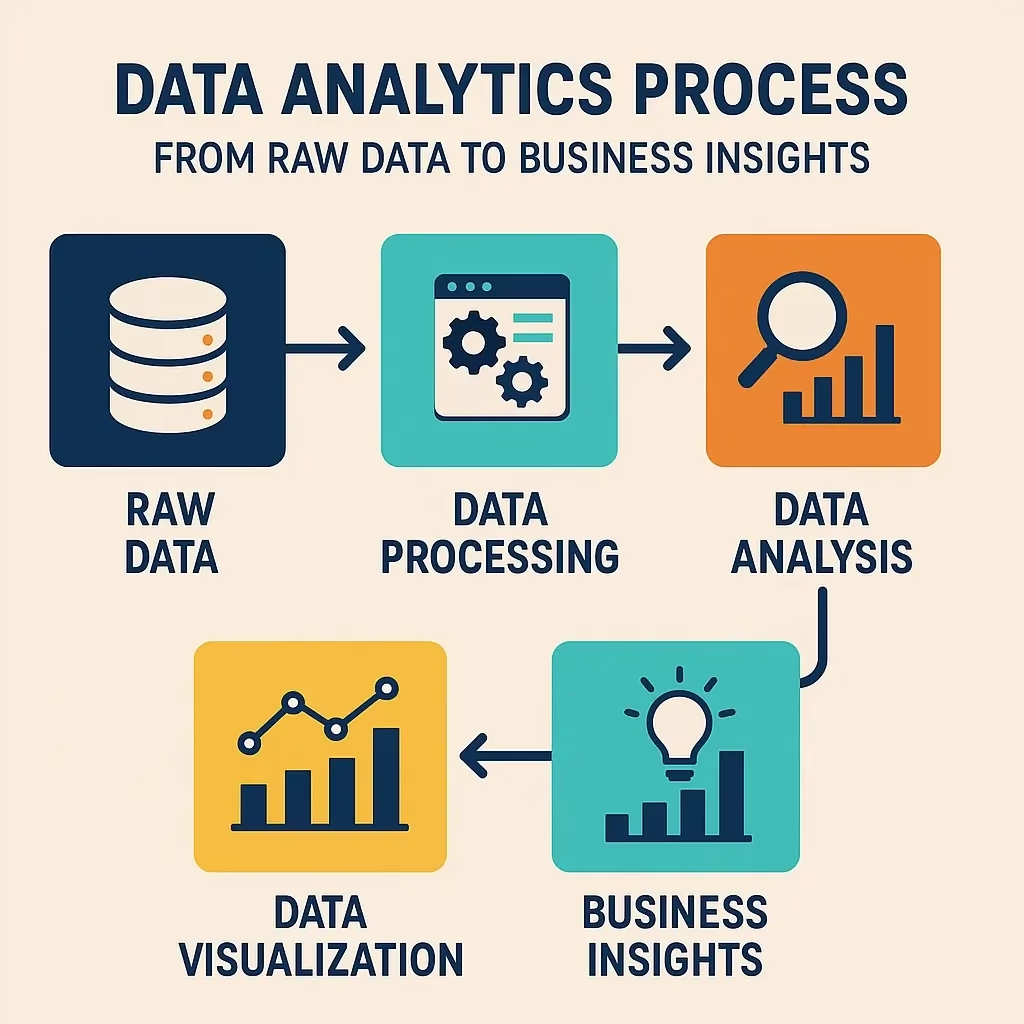
Problem to solve: Collect all data for the given or described goal.
Objective: The dataset is clean, consistent, and ready to be analysed.
Techniques used include:
Objective: Find the patterns and connections in the data we use to inform future analysis.
Common approaches include:
Tools used: Python, R, SQL, Excel, data visualization tools (Power BI, Tableau, etc.) or ML frameworks such as Scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
Objective: Uncover more advanced analysis and data-driven predictions or recommendations.
Analysts use tools like:
Objectif : visualiser les observations pour une prise de décision quantifiée d’information (= quantified decision making).
Objective: Go from insights to impactful business action.
Objective: Automate the analytics cycle for superior results.
If you have such desires or are planning to start a career in data analytics, or you want to take your skills to the next level, then you can think of doing data analyst training in Hyderabad. Through training, you will receive tools, experience, and hands-on projects that will ensure a successful career in this high-growth field.
Analytics Benchmark
Analytics benchmark is the Best Microsoft Technologies Training Institute In Hyderabad Provids Online & Classroom Training In Hyderabad and also Across the World by 15+ years of Industry experts.
Contact Us
Address
2nd floor, Balaji Towers, Aster Prime, Hospital street, Kumar Basti, Srinivasa Nagar, Ameerpet, Hyderabad, Telangana 500016.
Phone No:
+91-7799771214 | 91-7799771213
Email:
abtrainingshub@gmail.com